E.LThorndike.-Great philosopher and psychologist representative of pragmatism in philosophy and individualism in education. For education is primarily a function of individual nature, its purpose is tolerance respect for indivility and the formation of democratic consciousness.

John. Dewey.-He proposed a psychology of education as a discipline between behavioral sciences and educational practice taking experience as a starting point. He believes that a person learns by doing.He considers that education is a social and individual function. I thought that in school the child has to learn to live.
Emilio Mira y Lopez.-He focused his research on the subject of orientation and through them contributed to the development of the psychology of education decided to use special education.
Ivan Pavlov.-Representative of classical conditioning, achieved important advances within behaviorism.
Sigmund Freud.-Freud's contributions are valid because they provide explanations for certain behaviors of the student and the educator.
Friedrich Froebel.-The Development a theory to educate children through activity and action, I create educational toys to maintain active intelligence through the game.
Paulo Freire.-Proposes liberating education the educator must give prevalence to the dialogue with the student. The educator no longer only educates, he also learns through dialogue with the student.
Adolfo Ferriere.-The most enthusiastic defender and disseminator of the active school. His ideas were based on biological conceptions that later have been transformed into a spiritualist philosophy.
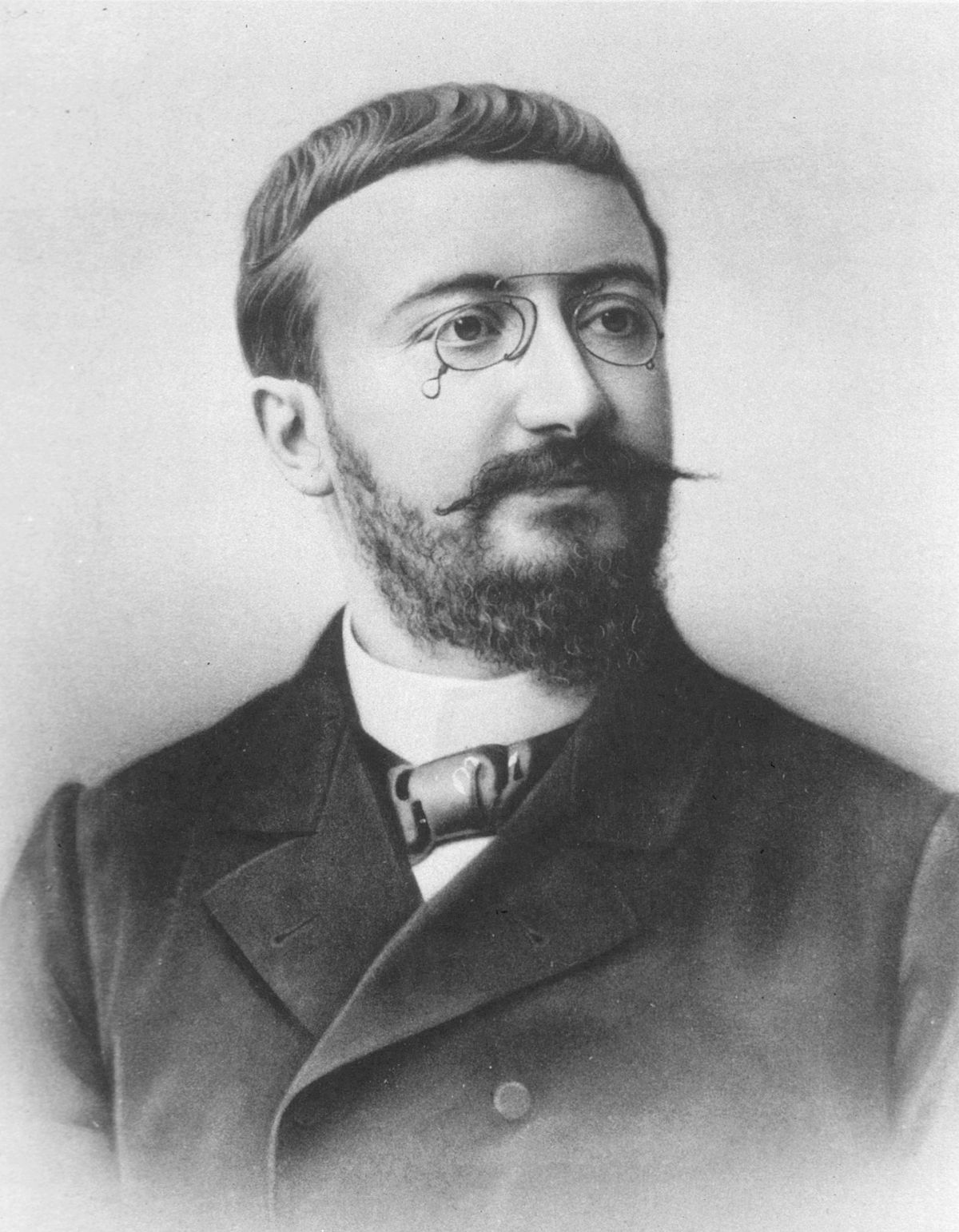
Alfred Binet.-He is the creator of the tests for the measurement of intelligence in children that serve to determine the mental age of the child. He also studied the memory of children and adults with special shortcomings. I contribute to the compression of how to value cognitive falcities.

Alfred Adler.-It represents the so-called individual psychology that is to say the individual behavior. I contribute to the pedagogy for the meaning it gives to the animic life of early childhood.
Alfred Binet.-He is the creator of the tests for the measurement of intelligence in children that serve to determine the mental age of the child. He also studied the memory of children and adults with special shortcomings. I contribute to the compression of how to value cognitive falcities.

Berthold Otto.-It represents the naturalistic pedagogy. Its two essential ideas are the "global teaching" and the education in"infantile language", according to this the language of the children must be studied and classified according to their age.
.jpg) Ovide Decroly.-It is based on the individual and collective activity of children but emphasizes their idea of the globalization of animistic life. Their conception of ideovisual reading starts with phrases and words instead of syllables and letters as ordinary methods.
Ovide Decroly.-It is based on the individual and collective activity of children but emphasizes their idea of the globalization of animistic life. Their conception of ideovisual reading starts with phrases and words instead of syllables and letters as ordinary methods.
.jpg) Ovide Decroly.-It is based on the individual and collective activity of children but emphasizes their idea of the globalization of animistic life. Their conception of ideovisual reading starts with phrases and words instead of syllables and letters as ordinary methods.
Ovide Decroly.-It is based on the individual and collective activity of children but emphasizes their idea of the globalization of animistic life. Their conception of ideovisual reading starts with phrases and words instead of syllables and letters as ordinary methods.
Maria Montessori.-This method consisted in giving the child freedom with responsibility in an environment prepared with the guidance of a specially trained person. When a child is ready to learn new and more difficult challenges, the guide helps him by providing the necessary means.
Lev Vigotsky.-The knowledge is not an object that is passed from one to another but is something that is built through operations and cognitive skills that are induced in social interaction. It points out the intellectual development of the individual can not be understood as independent of the social environment in which is the person immersed.
Jean Piaget.-He is a defender of new education and active school. Education should be based on the child's psychology and its active manifestations characteristic of childhood. Intelligence is the adaptation par excellence, the balance between continuous assimilation of things.
 Edouard Claparéde.- He was a biologist, he says that you have to study the child to be able to teach him. He is the author of the fincional pedagogy and said that childhood is the age of play and plasticity.
Edouard Claparéde.- He was a biologist, he says that you have to study the child to be able to teach him. He is the author of the fincional pedagogy and said that childhood is the age of play and plasticity.

G. Stanley Hall.- his research focused on children's education. his theories did not have much acceptance. I study the psychological changes of a person. he was the creator of the mental tests (intelligence).

W. T. Preyer .- He believed in the early development of children and in the theory that if the mother is intelligent, the child also. He considered that intelligence is inherited.
his research-experiment works were based on the analysis of smile, laughter, motor activity and children's dreams.

Emile Durkheim.- He believed that education is a social fact. it has to adapt the child to the social sphere. He said that education should not only be contained, but moral ideas.
Percy Nunn.- for education, it should be limited. the person must be educated for a personal contribution. He believed that the school is a select environment to improve their conditions.

Ellen Key.- she was not a pedagogue but she wrote a book called "the century of the child" in 1900, which was not accepted by other pedagogues. for her the most important thing was the child's life and she believed that the parents and the school drown out the individuality of the child.

W. A. Lay.- He was the cultivator of experimental pedagogy. He used experimental research methods. He agrees with the active pedagogy and defends it. he said: "the student has the right to give ideas and to contradict them"

William H. Kilpatrick.- he worked under the principles of contemporary pedagogy. to educate for life and to improve life. He created the first idea of project methods.

James Mark Baldwin.- he recovers intelligence a lot by inheritance, his theory is linked to genetics. He says that the genetic constitution is irreversible. his theory is based on motor and cognitive development, social interaction and personality development.

William James.- American, philosopher and psychologist. He trained the teachers. He believed in individual education that helps the human being to develop. the democratic consciousness is to say that it is allowed and not, such as being a good citizen and social and political life.
Hermanas Agazzi.- they were Italian pedagogues, they worked in the field of education. they believed that playful activity is important for learning. They founded a kindergarten.
 Edouard Claparéde.- He was a biologist, he says that you have to study the child to be able to teach him. He is the author of the fincional pedagogy and said that childhood is the age of play and plasticity.
Edouard Claparéde.- He was a biologist, he says that you have to study the child to be able to teach him. He is the author of the fincional pedagogy and said that childhood is the age of play and plasticity.
G. Stanley Hall.- his research focused on children's education. his theories did not have much acceptance. I study the psychological changes of a person. he was the creator of the mental tests (intelligence).

W. T. Preyer .- He believed in the early development of children and in the theory that if the mother is intelligent, the child also. He considered that intelligence is inherited.
his research-experiment works were based on the analysis of smile, laughter, motor activity and children's dreams.

Emile Durkheim.- He believed that education is a social fact. it has to adapt the child to the social sphere. He said that education should not only be contained, but moral ideas.
Percy Nunn.- for education, it should be limited. the person must be educated for a personal contribution. He believed that the school is a select environment to improve their conditions.

Ellen Key.- she was not a pedagogue but she wrote a book called "the century of the child" in 1900, which was not accepted by other pedagogues. for her the most important thing was the child's life and she believed that the parents and the school drown out the individuality of the child.

W. A. Lay.- He was the cultivator of experimental pedagogy. He used experimental research methods. He agrees with the active pedagogy and defends it. he said: "the student has the right to give ideas and to contradict them"

William H. Kilpatrick.- he worked under the principles of contemporary pedagogy. to educate for life and to improve life. He created the first idea of project methods.

James Mark Baldwin.- he recovers intelligence a lot by inheritance, his theory is linked to genetics. He says that the genetic constitution is irreversible. his theory is based on motor and cognitive development, social interaction and personality development.

William James.- American, philosopher and psychologist. He trained the teachers. He believed in individual education that helps the human being to develop. the democratic consciousness is to say that it is allowed and not, such as being a good citizen and social and political life.
Hermanas Agazzi.- they were Italian pedagogues, they worked in the field of education. they believed that playful activity is important for learning. They founded a kindergarten.

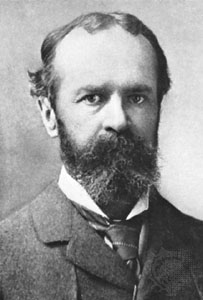

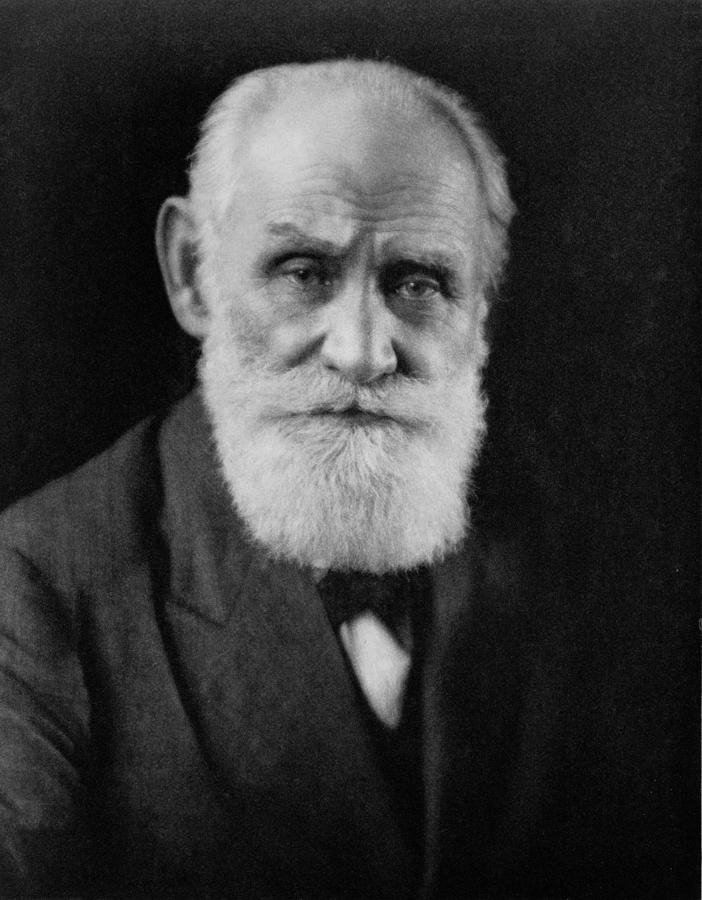











el conocer que muchas personas hicieron un gran aporte a la pedagogía de diferentes formas es importante saber y entender
ResponderEliminar